作用
在自定义 View 过程中,Layout 的主要作用就是计算 View 的位置。
计算
View的位置就是计算View的四个顶点位置:Left、Top、Right和Bottom。
layout 过程详解
layout 过程根据 View 的类型分为以下两种情况:
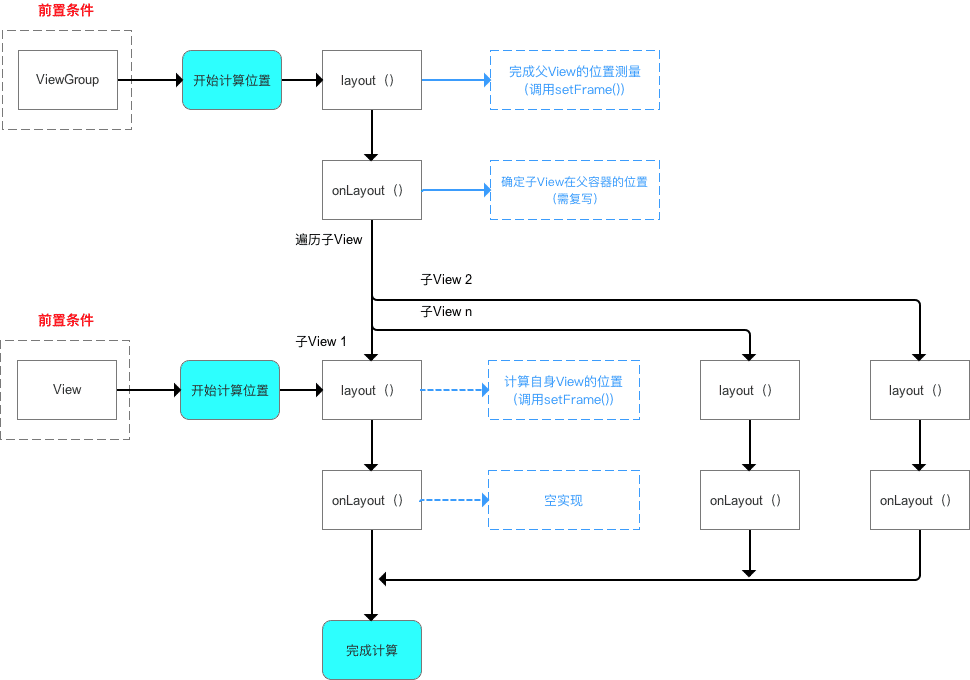
单一 View:仅计算View自身的位置。ViewGroup:除了计算View自身的位置外,还需要确定子View在父容器中的位置(遍历调用所有子元素的layout()和各子元素再递归去执行该流程)。
单一 View 的 layout 过程
应用场景
在没有现成的控件 View 满足需求、需自己实现时,则使用自定义单一 View。
使用方法
继承自 View、SurfaceView 或 其他 View;不包含子 View。
计算流程
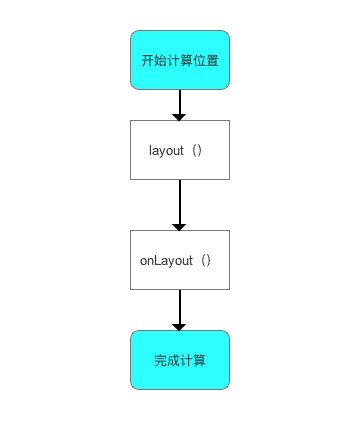
下面将 layout 过程中的方法进行详细分析:layout 过程入口为 layout()
/**
* 源码分析:layout()
* <p>
* 作用:确定 View 本身的位置,即设置 View 本身的四个顶点位置
*
* @param l 相对于父视图的左侧位置
* @param t 相对于父视图的顶部位置
* @param r 相对于父视图的右侧位置
* @param b 相对于父视图的底部位置
*/
public void layout(int l, int t, int r, int b) {
// 当前视图的四个顶点
int oldL = mLeft;
int oldT = mTop;
int oldB = mBottom;
int oldR = mRight;
// 1. 确定View的位置:setFrame() / setOpticalFrame()
// 即初始化四个顶点的值、判断当前View大小和位置是否发生了变化并返回
// ->>分析1、分析2
boolean changed = isLayoutModeOptical(mParent) ?
setOpticalFrame(l, t, r, b) : setFrame(l, t, r, b);
// 2. 若视图的大小和位置发生变化,会重新确定该View所有的子View在父容器的位置:onLayout()
if (changed || (mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_LAYOUT_REQUIRED) == PFLAG_LAYOUT_REQUIRED) {
onLayout(changed, l, t, r, b);
// 对于单一View的laytou过程:由于单一View是没有子View的,故onLayout()是一个空实现->>分析3
// 对于ViewGroup的laytou过程:由于确定位置与具体布局有关,所以onLayout()在ViewGroup为一个抽象方法,需重写实现
...
}
...
}
/**
* 分析1:setFrame()
* <p>
* 作用:根据传入的4个位置值,设置View本身的四个顶点位置,最终确定View本身的位置
*
* @param left 相对于父视图的左侧位置
* @param top 相对于父视图的顶部位置
* @param right 相对于父视图的右侧位置
* @param bottom 相对于父视图的底部位置
*/
protected boolean setFrame(int left, int top, int right, int bottom) {
boolean changed = false;
if (mLeft != left || mRight != right || mTop != top || mBottom != bottom) {
changed = true;
...
// 通过以下赋值语句记录下了视图的位置信息,即确定View的四个顶点,从而确定了视图的位置
mLeft = left;
mTop = top;
mRight = right;
mBottom = bottom;
mRenderNode.setLeftTopRightBottom(mLeft, mTop, mRight, mBottom);
...
}
return changed;
}
/**
* 分析2:setOpticalFrame()
* <p>
* 作用:根据传入的4个位置值,设置View本身的四个顶点位置,最终确定View本身的位置
*
* @param left 相对于父视图的左侧位置
* @param top 相对于父视图的顶部位置
* @param right 相对于父视图的右侧位置
* @param bottom 相对于父视图的底部位置
*/
private boolean setOpticalFrame(int left, int top, int right, int bottom) {
Insets parentInsets = mParent instanceof View ?
((View) mParent).getOpticalInsets() : Insets.NONE;
Insets childInsets = getOpticalInsets();
// 内部实际上是调用setFrame()
return setFrame(
left + parentInsets.left - childInsets.left,
top + parentInsets.top - childInsets.top,
right + parentInsets.left + childInsets.right,
bottom + parentInsets.top + childInsets.bottom);
}
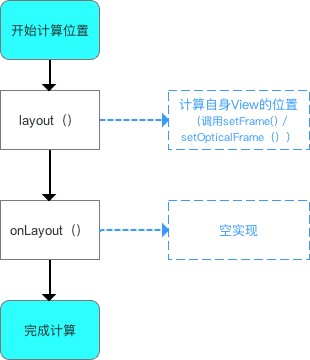
/**
* 分析3:onLayout()
* <p>
* 注:对于单一View的laytou过程
* a. 由于单一View是没有子View的,故onLayout()是一个空实现
* b. 由于在layout()中已经对自身View进行了位置计算,所以单一View的layout过程在layout()后就已完成
*
* @param changed 当前View的大小和位置是否改变了
* @param left 相对于父视图的左侧位置
* @param top 相对于父视图的顶部位置
* @param right 相对于父视图的右侧位置
* @param bottom 相对于父视图的底部位置
*/
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int left, int top, int right, int bottom) {
}
总结
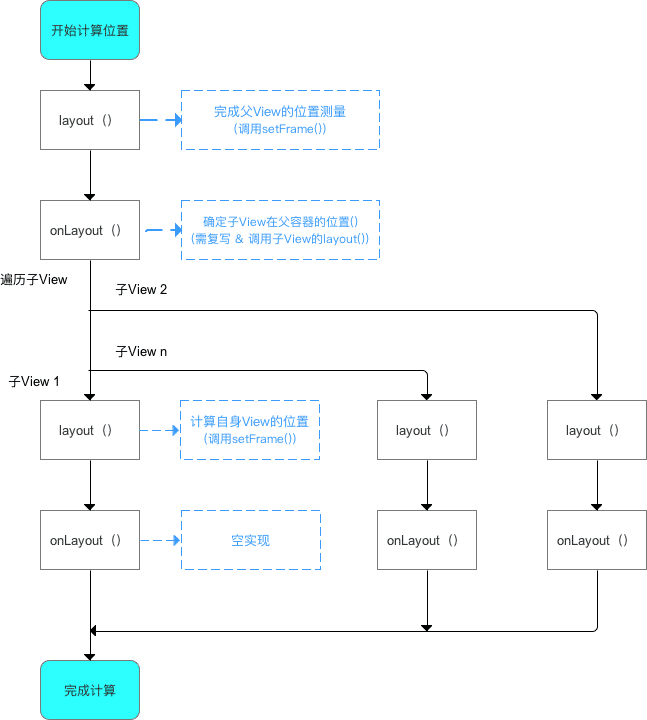
ViewGroup 的 layout 过程
应用场景
利用现有的组件根据特定的布局方式来组成新的组件。
使用方法
继承自 ViewGroup 或各种 Layout;包含子 View。
计算原理
自上而下、一层层地传递下去,直到完成整个 View 树的 layout() 过程:
- 计算自身
ViewGroup的位置:layout()。 - 遍历所有子
View并确定子View自身在ViewGroup中的位置(调用子View的layout()方法):onLayout()。

计算流程
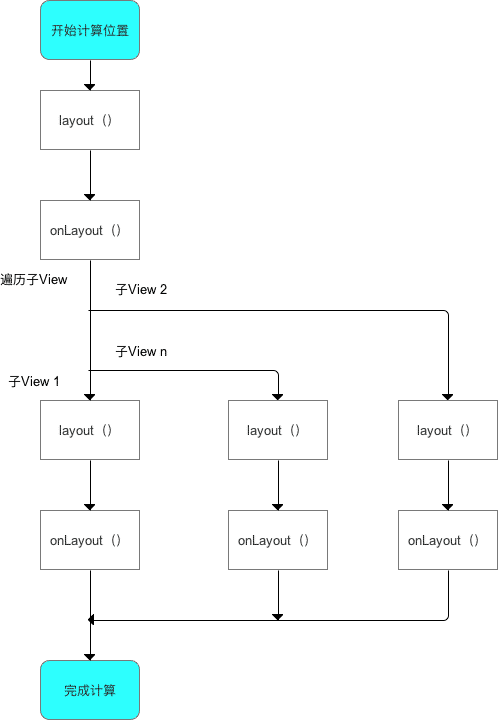
ViewGroup 和 View 同样拥有 layout() 和 onLayout(),但二者不同的:
- 一开始计算
ViewGroup位置时,调用的是ViewGroup的layout()和onLayout(); - 当开始遍历子
View并计算子View位置时,调用的是子View的layout()和onLayout()。
下面将 layout 过程中的方法进行详细分析:layout 过程入口为 layout()
/**
* 源码分析:layout()
* <p>
* 作用:确定 View 本身的位置,即设置 View 本身的四个顶点位置
*
* @param l 相对于父视图的左侧位置
* @param t 相对于父视图的顶部位置
* @param r 相对于父视图的右侧位置
* @param b 相对于父视图的底部位置
*/
public void layout(int l, int t, int r, int b) {
// 当前视图的四个顶点
int oldL = mLeft;
int oldT = mTop;
int oldB = mBottom;
int oldR = mRight;
// 1. 确定View的位置:setFrame() / setOpticalFrame()
// 即初始化四个顶点的值、判断当前View大小和位置是否发生了变化并返回
// ->>分析1、分析2
boolean changed = isLayoutModeOptical(mParent) ?
setOpticalFrame(l, t, r, b) : setFrame(l, t, r, b);
// 2. 若视图的大小和位置发生变化,会重新确定该View所有的子View在父容器的位置:onLayout()
if (changed || (mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_LAYOUT_REQUIRED) == PFLAG_LAYOUT_REQUIRED) {
onLayout(changed, l, t, r, b);
// 对于单一View的laytou过程:由于单一View是没有子View的,故onLayout()是一个空实现->>分析3
// 对于ViewGroup的laytou过程:由于确定位置与具体布局有关,所以onLayout()在ViewGroup为一个抽象方法,需重写实现
...
}
...
}
/**
* 分析1:setFrame()
* <p>
* 作用:根据传入的4个位置值,设置View本身的四个顶点位置,最终确定View本身的位置
*
* @param left 相对于父视图的左侧位置
* @param top 相对于父视图的顶部位置
* @param right 相对于父视图的右侧位置
* @param bottom 相对于父视图的底部位置
*/
protected boolean setFrame(int left, int top, int right, int bottom) {
boolean changed = false;
if (mLeft != left || mRight != right || mTop != top || mBottom != bottom) {
changed = true;
...
// 通过以下赋值语句记录下了视图的位置信息,即确定View的四个顶点,从而确定了视图的位置
mLeft = left;
mTop = top;
mRight = right;
mBottom = bottom;
mRenderNode.setLeftTopRightBottom(mLeft, mTop, mRight, mBottom);
...
}
return changed;
}
/**
* 分析2:setOpticalFrame()
* <p>
* 作用:根据传入的4个位置值,设置View本身的四个顶点位置,最终确定View本身的位置
*
* @param left 相对于父视图的左侧位置
* @param top 相对于父视图的顶部位置
* @param right 相对于父视图的右侧位置
* @param bottom 相对于父视图的底部位置
*/
private boolean setOpticalFrame(int left, int top, int right, int bottom) {
Insets parentInsets = mParent instanceof View ?
((View) mParent).getOpticalInsets() : Insets.NONE;
Insets childInsets = getOpticalInsets();
// 内部实际上是调用setFrame()
return setFrame(
left + parentInsets.left - childInsets.left,
top + parentInsets.top - childInsets.top,
right + parentInsets.left + childInsets.right,
bottom + parentInsets.top + childInsets.bottom);
}
/**
* 分析3:onLayout()
* <p>
* 注:对于单一View的laytou过程
* a. 由于单一View是没有子View的,故onLayout()是一个空实现
* b. 由于在layout()中已经对自身View进行了位置计算,所以单一View的layout过程在layout()后就已完成
* c. 复写原理:遍历子View、计算当前子View的四个位置值并确定自身子View的位置(调用子 View 的 layout() 方法)
*
* @param changed 当前View的大小和位置是否改变了
* @param left 相对于父视图的左侧位置
* @param top 相对于父视图的顶部位置
* @param right 相对于父视图的右侧位置
* @param bottom 相对于父视图的底部位置
*/
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int left, int top, int right, int bottom) {
// 1. 遍历子View:循环所有子View
for (int i = 0; i < getChildCount(); i++) {
View child = getChildAt(i);
// 2. 计算当前子View的四个位置值
// 2.1 位置的计算逻辑,需自己实现,也是自定义View的关键
...
// 2.2 对计算后的位置值进行赋值
int mLeft = left;
int mTop = top;
int mRight = right;
int mBottom = bottom;
// 3. 根据上述4个位置的计算值,设置子View的4个顶点:调用子view的layout() & 传递计算过的参数
// 即确定了子View在父容器的位置
child.layout(mLeft, mTop, mRight, mBottom);
// 该过程类似于单一View的layout过程中的layout()和onLayout(),此处不作过多描述
}
}
总结
总结