一个 Context 意味着一个场景,一个场景就是用户和软件进行交互的一个过程。那么从安卓程序的角度来看,Context 是什么?其实一个 Activity 就是一个 Context,一个 Service 也是一个 Context。
Context 简介
Context 的类关系图如下: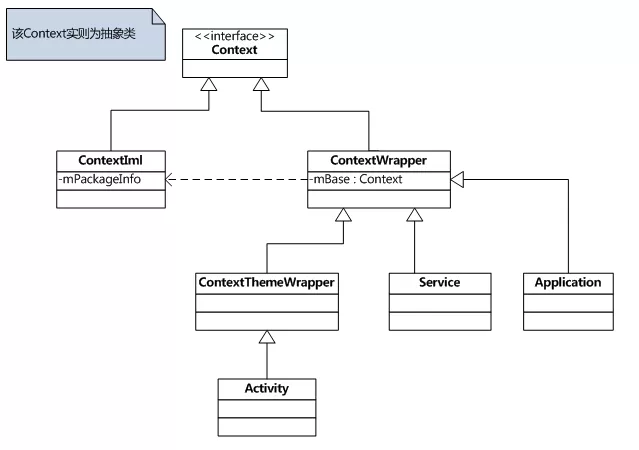
Context 本身是一个抽象类,有两个直系子类,一个是 ContextWrapper,一个是 ContextImpl。
从类名称上就可以看出,ContextWrapper 是 Context 的代理类,而 ContextImpl 则是 Context 的实现类。另外 ContextWrapper 有三个直接的子类 ContextThemeWrapper、Service 和 Application,其中 ContextThemeWrapper 是一个带主题的封装类,而它有一个直接子类就是 Activity。
Context 数量
一个应用程序中到底有多少个 Context 呢?
其实根据上面的 Context类型就已经可以得出答案了。Context 一共有 Application、Activity 和 Service 三种类型,因此一个应用程序中 Context 数量的计算公式就可以这样写:
Context 数量 = Activity 数量 + Service 数量 + 1
上面的 1 代表着 Application 的数量,因为一个应用程序中可以有多个 Activity 和多个 Service,但是只能有一个 Application。当然,这只是普通情况,不考虑多进程或其他因素的影响。
Context 功能
Context 到底可以实现哪些功能呢?这个就实在是太多了,弹出 Toast、启动 Activity、启动 Service、发送广播、操作数据库等都需要用到 Context。
由于 Context 的具体能力是由 ContextImpl 类去实现的,因此在绝大多数场景下,Activity、Service 和 Application 这三种类型的 Context 都是可以通用的。
不过有几种场景比较特殊,比如启动 Activity,还有弹出 Dialog。出于安全原因的考虑,Android 是不允许 Activity 或 Dialog 凭空出现的。Activity 的启动必须要建立在另一个 Activity 的基础之上,也就是以此形成的返回栈。而 Dialog 则必须在一个 Activity 上面弹出(除非是 System Alert 类型的 Dialog),因此在这种场景下,只能使用 Activity 类型的 Context,否则将会出错。
Context 作用
要想知道 Context 的作用,首先先看一下 Context 提供的方法:
public abstract class Context {
// 四大组件相关
public abstract void startActivity(Intent intent);
public abstract void startActivity(Intent intent, @Nullable Bundle options);
public abstract void startActivities(Intent[] intents);
public abstract void startActivities(Intent[] intents, Bundle options);
public abstract void sendBroadcast(Intent intent);
public abstract void sendBroadcast(Intent intent, @Nullable String receiverPermission);
public abstract void sendOrderedBroadcast(Intent intent, String receiverPermission);
public abstract Intent registerReceiver(BroadcastReceiver receiver, IntentFilter filter);
public abstract void unregisterReceiver(BroadcastReceiver receiver);
public abstract ComponentName startService(Intent service);
public abstract ComponentName startForegroundService(Intent service);
public abstract boolean stopService(Intent service);
public abstract boolean bindService(Intent service, ServiceConnection conn, int flags);
public abstract void unbindService(@NonNull ServiceConnection conn);
public abstract ContentResolver getContentResolver();
// 获取系统资源
public abstract AssetManager getAssets();
public abstract Resources getResources();
public abstract PackageManager getPackageManager();
public abstract ClassLoader getClassLoader();
public abstract Context getApplicationContext();
public abstract Context createConfigurationContext(Configuration overrideConfiguration);
public abstract Context createDisplayContext(@NonNull Display display);
public abstract @Nullable Object getSystemService(@ServiceName @NonNull String name);
public final @Nullable <T> T getSystemService(@NonNull Class<T> serviceClass);
// 获取应用资源
public final CharSequence getText(@StringRes int resId);
public final String getString(@StringRes int resId);
public final String getString(@StringRes int resId, Object... formatArgs);
public final int getColor(@ColorRes int id);
public final Drawable getDrawable(@DrawableRes int id);
public final ColorStateList getColorStateList(@ColorRes int id);
public abstract void setTheme(@StyleRes int resid);
public abstract Resources.Theme getTheme();
public final TypedArray obtainStyledAttributes(@NonNull int[] attrs);
public final TypedArray obtainStyledAttributes(@StyleRes int resid, int[] attrs);
// 获取应用相关信息
public String getOpPackageName();
public Executor getMainExecutor();
public abstract Looper getMainLooper();
public abstract String getPackageName();
public abstract ApplicationInfo getApplicationInfo();
public abstract String getPackageResourcePath();
public abstract String getPackageCodePath();
public abstract @Nullable String getSystemServiceName(@NonNull Class<?> serviceClass);
public abstract int checkPermission(@NonNull String permission, int pid, int uid);
public abstract int checkSelfPermission(@NonNull String permission);
// 文件相关
public abstract boolean deleteFile(String name);
public abstract File getDataDir();
public abstract File getFilesDir();
public abstract File getNoBackupFilesDir();
public abstract File getExternalFilesDir(@Nullable String type);
public abstract File[] getExternalFilesDirs(String type);
public abstract File getObbDir();
public abstract File[] getObbDirs();
public abstract File getCacheDir();
public abstract File getCodeCacheDir();
public abstract File getExternalCacheDir();
public abstract File[] getExternalCacheDirs();
public abstract File[] getExternalMediaDirs();
public abstract SharedPreferences getSharedPreferences(String name, int mode);
public abstract boolean moveSharedPreferencesFrom(Context sourceContext, String name);
public abstract void reloadSharedPreferences();
public abstract FileInputStream openFileInput(String name);
public abstract FileOutputStream openFileOutput(String name, @FileMode int mode);
// 数据库相关
public abstract SQLiteDatabase openOrCreateDatabase(String name, int mode, CursorFactory f);
public abstract boolean deleteDatabase(String name);
public abstract String[] databaseList();
// 其他
public void registerComponentCallbacks(ComponentCallbacks callback);
public void unregisterComponentCallbacks(ComponentCallbacks callback);
}
根据 Context 的源码可以发现,Context 就相当于 Application 的大管家,主要负责:
- 四大组件的交互:包括启动
Activity、Broadcast、Service,获取ContentResolver等; - 获取系统资源:包括获取
AssetManager、PackageManager、Resources、System Service等; - 获取应用资源:包括获取
color、string、drawable、theme等; - 文件相关:包括获取各种应用目录、
SharedPreference、删除文件等; - 数据库相关:包括打开数据库、删除数据库、获取数据库路径等;
- 其它辅助功能:比如设置
ComponentCallbacks,即监听配置信息改变、内存不足等事件的发生。
Context 区别
ContextWrapper
/**
* Proxying implementation of Context that simply delegates all of its calls to
* another Context. Can be subclassed to modify behavior without changing
* the original Context.
*/
public class ContextWrapper extends Context {
@UnsupportedAppUsage
Context mBase; // 注意这个成员
public ContextWrapper(Context base) {
mBase = base;
}
/**
* Set the base context for this ContextWrapper. All calls will then be
* delegated to the base context. Throws
* IllegalStateException if a base context has already been set.
*
* @param base The new base context for this wrapper.
*/
protected void attachBaseContext(Context base) {
if (mBase != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Base context already set");
}
mBase = base;
}
/**
* @return the base context as set by the constructor or setBaseContext
*/
public Context getBaseContext() {
return mBase;
}
@Override
public AssetManager getAssets() {
return mBase.getAssets();
}
@Override
public Resources getResources() {
return mBase.getResources();
}
@Override
public PackageManager getPackageManager() {
return mBase.getPackageManager();
}
@Override
public ContentResolver getContentResolver() {
return mBase.getContentResolver();
}
...
}
可以看到,ContextWrapper 实际上就是 Context 的代理类而已,所有的操作都是通过内部成员 mBase 完成的。另外,Activity、Service 的 getBaseContext() 方法返回的就是这个 mBase 对象。
ContextThemeWrapper
/**
* A context wrapper that allows you to modify or replace the theme of the wrapped context.
*/
public class ContextThemeWrapper extends ContextWrapper {
private int mThemeResource;
private Resources.Theme mTheme;
private LayoutInflater mInflater;
private Configuration mOverrideConfiguration;
private Resources mResources;
public ContextThemeWrapper() {
super(null);
}
public ContextThemeWrapper(Context base, @StyleRes int themeResId) {
super(base);
mThemeResource = themeResId;
}
public ContextThemeWrapper(Context base, Resources.Theme theme) {
super(base);
mTheme = theme;
}
@Override
protected void attachBaseContext(Context newBase) {
super.attachBaseContext(newBase);
}
/**
* 在Recource初始化之前,传入配置信息
*/
public void applyOverrideConfiguration(Configuration overrideConfiguration) {
if (mResources != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"getResources() or getAssets() has already been called");
}
if (mOverrideConfiguration != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Override configuration has already been set");
}
mOverrideConfiguration = new Configuration(overrideConfiguration);
}
@Override
public Resources getResources() {
return getResourcesInternal();
}
private Resources getResourcesInternal() {
if (mResources == null) {
if (mOverrideConfiguration == null) {
mResources = super.getResources();
} else if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= 17) {
// 根据配置信息初始化 Resource
// 注意,这里创建了另一个和 Base Context 不同的 Resource
final Context resContext = createConfigurationContext(mOverrideConfiguration);
mResources = resContext.getResources();
}
}
return mResources;
}
@Override
public void setTheme(int resid) {
if (mThemeResource != resid) {
mThemeResource = resid;
initializeTheme();
}
}
@Override
public Resources.Theme getTheme() {
// 只会初始化一次
if (mTheme != null) {
return mTheme;
}
if (mThemeResource == 0) {
mThemeResource = R.style.Theme_AppCompat_Light;
}
initializeTheme();
return mTheme;
}
/**
* 初始化Theme
*/
private void initializeTheme() {
final boolean first = mTheme == null;
if (first) {
// 根据 Resource 获取 Theme
mTheme = getResources().newTheme();
// 复制内容
Resources.Theme theme = getBaseContext().getTheme();
if (theme != null) {
mTheme.setTo(theme);
}
}
onApplyThemeResource(mTheme, mThemeResource, first);
}
protected void onApplyThemeResource(Resources.Theme theme, int resid, boolean first) {
theme.applyStyle(resid, true);
}
@Override
public Object getSystemService(String name) {
if (LAYOUT_INFLATER_SERVICE.equals(name)) {
if (mInflater == null) {
mInflater = LayoutInflater.from(getBaseContext()).cloneInContext(this);
}
return mInflater;
}
return getBaseContext().getSystemService(name);
}
@Override
public AssetManager getAssets() {
return getResources().getAssets();
}
}
结合注释及源码,可以发现,ContextThemeWrapper 内部包含了与主题相关的接口,有自己的 Theme 和 Resource 成员,并且 Resource 可以传入自己的配置初始化。即 Theme 和 Resource 相关的行为不再是直接调用 mBase 的方法了,也就说,ContextThemeWrapper 和它的 mBase 成员在 Resource 和 Theme 相关的行为上是不同的。
ContextImpl
/**
* Common implementation of Context API, which provides the base
* context object for Activity and other application components.
*/
class ContextImpl extends Context {
private Resources mResources;
private int mThemeResource = 0;
private Resources.Theme mTheme = null;
@Override
public Resources getResources() {
return mResources;
}
void setResources(Resources r) {
if (r instanceof CompatResources) {
((CompatResources) r).setContext(this);
}
mResources = r;
}
@Override
public void setTheme(int resId) {
synchronized (mSync) {
if (mThemeResource != resId) {
mThemeResource = resId;
initializeTheme();
}
}
}
@Override
public int getThemeResId() {
synchronized (mSync) {
return mThemeResource;
}
}
@Override
public Resources.Theme getTheme() {
synchronized (mSync) {
if (mTheme != null) {
return mTheme;
}
mThemeResource = Resources.selectDefaultTheme(mThemeResource,
getOuterContext().getApplicationInfo().targetSdkVersion);
initializeTheme();
return mTheme;
}
}
/**
* 初始化Theme
*/
private void initializeTheme() {
if (mTheme == null) {
mTheme = mResources.newTheme();
}
mTheme.applyStyle(mThemeResource, true);
}
private static Resources createResources(...) {
return ResourcesManager.getInstance().getResources(...);
}
static ContextImpl createSystemContext(... {
LoadedApk packageInfo = new LoadedApk(mainThread);
ContextImpl context = new ContextImpl(...);
context.setResources(packageInfo.getResources());
return context;
}
static ContextImpl createAppContext(...) {
if (packageInfo == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("packageInfo");
ContextImpl context = new ContextImpl(...);
context.setResources(packageInfo.getResources());
return context;
}
static ContextImpl createActivityContext(...) {
ContextImpl context = new ContextImpl(...);
final ResourcesManager resourcesManager = ResourcesManager.getInstance();
context.setResources(resourcesManager.createBaseActivityResources(...));
return context;
}
}
从代码中可以看出,ContextImpl 真正实现了 Context 中所有的方法,另外,ContextImpl 可以用于创建 Activity、Service 以及 Application 的 mBase 成员。
不同组件创建 ContextImpl 的方式:
Activity:调用ActivityThread.createBaseContextForActivity()方法;Service/Application:**调用ContextImpl.createAppContext()方法;Provider:**调用ContextImpl.createPackageContext()方法;BroadcastReceiver:**调用Application.getBaseContext()方法。
总结
Context 的继承关系如下: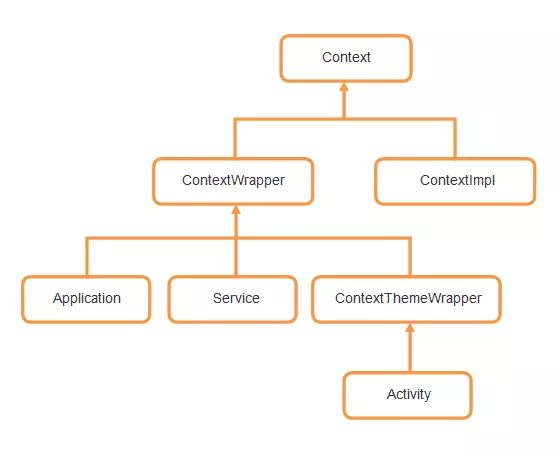
ContextWrapper、ContextThemeWrapper都是Context的代理类,二者的区别在于ContextThemeWrapper有自己的Theme以及Resource,并且Resource可以传入自己的配置初始化;ContextImpl是Context的主要实现类,Activity、Service和Application的Base Context都是由它创建的,即ContextWrapper代理的就是ContextImpl对象本身;Activity、Service和Application的Base Context都是由ContextImpl创建的,且创建的都是ContextImpl对象,即它们都是ContextImpl的代理类;Service和Application使用同一个Recource,和Activity使用的Resource不同。



